Culture & Lifestyle
When stress turns physical
Conversion disorder is a mental health condition where psychological distress manifests as physical symptoms like paralysis or blindness.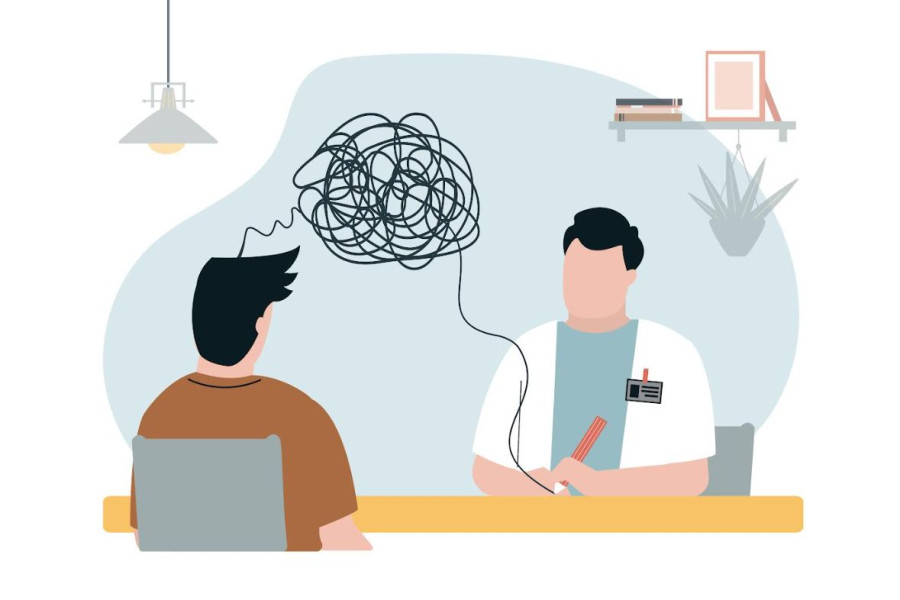
Sanskriti Pokharel
Imagine waking up one day, unable to move your arm, speak clearly, or even see, with medical tests revealing no physical cause for these symptoms. While this might sound abstract, it is a stark reality for those living with conversion disorder. Gaining a deeper understanding of this condition is vital—not just for those directly affected but also for their families and communities.
Kamala Paudel, a psychosocial counsellor with the Centre for Mental Health & Counselling-Nepal (CMC) under the Karnali Mental Health Project, sheds light on conversion disorder, its causes, and preventive measures individuals can take.
What is conversion disorder?
Conversion Disorder, now known as functional neurological symptom disorder (FNSD) in the DSM-5, is a mental health condition where individuals experience neurological symptoms (such as paralysis, blindness, or seizures) that medical tests or physical findings cannot explain. These symptoms cause significant distress or impairment but are thought to arise from psychological factors rather than a medical or neurological disease.
What are the most common triggers or causes of conversion disorder?
Conversion disorder often stems from a combination of emotional stress and psychological factors. Common triggers include significant life stress or trauma, such as accidents, abuse, or the loss of a loved one, which can deeply impact an individual.
Repressed emotions and unresolved psychological conflicts may also surface as physical symptoms while underlying conditions like anxiety or depression can increase vulnerability. Difficult relationships or family conflicts can add to the emotional strain, and societal stigma around mental health can sometimes cause individuals to express their distress through physical manifestations unconsciously.

Is this disorder more common in women?
Yes, studies show that conversion disorder tends to be more common in women, and a mix of biological, social, and cultural factors can influence this. Women are often under more pressure to hide or suppress emotional distress, which might lead them to express their feelings through physical symptoms instead.
Hormonal differences and societal expectations around gender roles also contribute, as women may be more likely to face challenges when it comes to openly discussing or addressing their emotional struggles.
Are individuals with conversion disorder prone to relapse?
Individuals diagnosed with conversion disorder are particularly susceptible to experiencing relapses, especially in circumstances where specific stressors are not effectively managed or addressed. The presence of unresolved trauma or emotional conflicts can significantly contribute to the likelihood of recurrence, as these underlying issues may remain unacknowledged and unprocessed.
Furthermore, a lack of social support or therapeutic assistance can exacerbate the situation. It will leave individuals without the necessary resources to cope with their symptoms and emotional challenges. Thus, addressing these factors is crucial for reducing the risk of relapse in those affected by conversion disorder.
What steps can individuals or communities take to prevent conversion disorder?
Individuals and communities can implement several proactive strategies to prevent conversion disorder effectively. For individuals, it is essential to focus on stress management by developing healthy coping mechanisms such as mindfulness practices, regular physical exercise, and engaging in creative activities that promote emotional expression. Seeking emotional support is also vital; individuals should foster open communication with friends and family and consider professional help when dealing with psychological distress.
Additionally, cultivating self-awareness allows individuals to recognise and address emotional conflicts or stressors before they escalate into more serious issues.
For communities, promoting mental health awareness plays a crucial role in reducing the stigma associated with mental health challenges through education and advocacy efforts. Ensuring that counselling services are readily accessible in schools, workplaces, and local communities can provide essential resources for those in need.
Furthermore, communities should aim to encourage resilience by creating supportive environments that teach skills related to emotional regulation, problem-solving, and effective communication. Finally, offering specialised support for trauma survivors is critical to addressing unresolved stressors that could otherwise manifest as physical symptoms. By focusing on early identification and adopting a holistic approach, the risk of developing conversion disorder can be significantly reduced, leading to better overall mental health outcomes.




 9.7°C Kathmandu
9.7°C Kathmandu
.jpg&w=200&height=120)













