Columns
Much talk, little action
Most points in the Inter-Provincial Council decisions have not been implemented.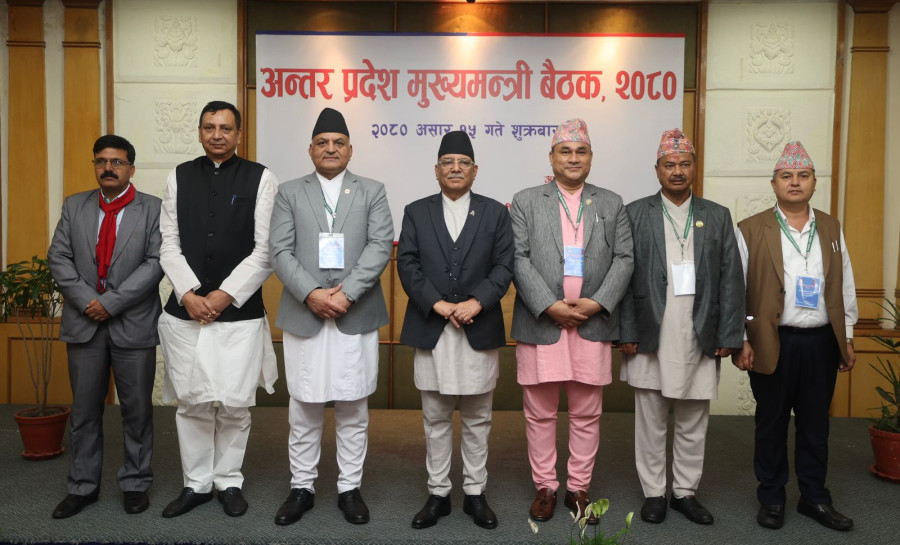
Khim Lal Devkota
On July 21, House Speaker Dev Raj Ghimire, Deputy Speaker Indira Ranamagar, National Assembly Chairperson Ganesh Prasad Timilsina, Deputy Chairperson Urmila Aryal and the speakers and deputy speakers of all seven Provincial Assemblies met in Kathmandu and made 12 significant decisions and recommendations to make law enforcement more effective. The gathering also agreed to establish a parliamentary mechanism to implement constitutionally guaranteed women's rights and promote women's empowerment.
The Parliamentary Special Committee on the Implementation of Federalism has issued a report covering political federalism, administrative federalism, fiscal federalism, intergovernmental coordination and cooperation, and good governance. The report contains 99 recommendations including reducing the number of federal and provincial ministries.
On July 1, the National Coordinating Council met in Pokhara with the heads of the three levels of the executive branch taking part.
The National Coordinating Council plays a crucial role in intergovernmental relations between the three tiers of government. It facilitates the formulation of laws and policies on matters of concurrent powers; coordinates issues concerning national interest and implementation at the subnational levels; resolves complexities related to the implementation of national plans, policies and laws at the subnational levels; formulates laws, policies and strategies that affect the provinces and the local levels; coordinates the implementation of large projects at the inter-provincial level; reviews and analyses the policies, laws and plans formulated at the federal level; and carries out necessary activities to maintain harmony in service delivery at the federal units.
The council needs to meet at least once a year but no meeting has been held since the law became effective in July 2020.
Dispute resolution
Nepal has several inter-governmental relationship entities including the Inter-Provincial Council. The council serves as a dispute resolution body between the federal and provincial governments or between different provincial governments. It consists of the prime minister, finance minister, home minister and the chief ministers of the provinces. The first and second meetings of the Inter-Provincial Council were held in December 2018. A detailed Federalism Implementation Action Plan with 29 thematic areas was approved at the meeting. These first and second meetings were milestones for implementing federalism in Nepal. The third Inter-Provincial Council meeting took place in April 2019, and no meetings have been held since then.
Nepal has set up other inter-governmental relationship entities such as the Provincial Coordination Council, Inter-Governmental Fiscal Council and Ministerial Level Sectoral Committee. Many federal countries like the United States, Canada, Germany, Australia, Switzerland and Brazil do not have formal inter-governmental coordination entities. Instead, they rely on informal discussions and collaboration to strengthen relations between the different levels of government. As demonstrated by these countries, having fewer organisations, holding fewer meetings and focusing on collaborative efforts can be more beneficial.
The National Coordinating Council has made significant decisions. They include removing ambiguity and duplication in the implementation process among the federal units (federal, provincial and local levels), cooperating while creating laws related to rights in the concurrent list, formulating and implementing laws essential for federalism's successful implementation, improving human resource management and service delivery, guaranteeing a minimum two-year posting for the chief executive officer of any local level and one-year posting for employees stationed in the provinces, streamlining the process of land acquisition required for subnational infrastructure construction, and making amendments to the laws.
The meeting has also established a committee chaired by the secretary of the Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers to clarify the powers of federal units by revising the functional responsibility-related “unbundling report”. Similarly, another committee, under the coordination of the secretary of the National Planning Commission, has been formed to study grants allocated by federal units for various organisations and programmes of the same nature. The committee will prepare suggestions and submit a report within a month. Additionally, a committee has been set up, coordinated by the secretary of the Office of the Prime Minister and Council of Ministers, to recommend the removal of duplication-related structures.
No implementation
The decisions made at the meeting are commendable, but their successful implementation remains to be seen. Unfortunately, most of the activities outlined in the 29 Inter-Provincial Council decisions have not been carried out. This raises concerns about the potential implementation of the National Coordinating Council decisions, especially considering the delay in executing the Inter-Provincial Council decisions which were supposed to be completed within one or two years after the meeting.
For instance, the Inter-Provincial Council meeting held in 2018 had decided to approve the civil service law by mid-March 2019, but it has not happened. The Inter-Provincial Council had also planned to formulate laws related to concurrent rights at the three levels by mid-April 2019. This has not been implemented, along with many other activities outlined in the Federalism Implementation Action Plan.
In light of these circumstances, it was necessary and important for the National Coordinating Council meeting to review the decisions made by the Inter-Provincial Council and assess the status of their implementation. Taking stock of the progress can provide valuable insights into addressing any potential challenges and ensuring effective implementation of the National Coordinating Council decisions.




 23.88°C Kathmandu
23.88°C Kathmandu