Culture & Lifestyle
Understanding warts
Dr Isha Poudel Koirala gives an insight into this common but misunderstood skin condition.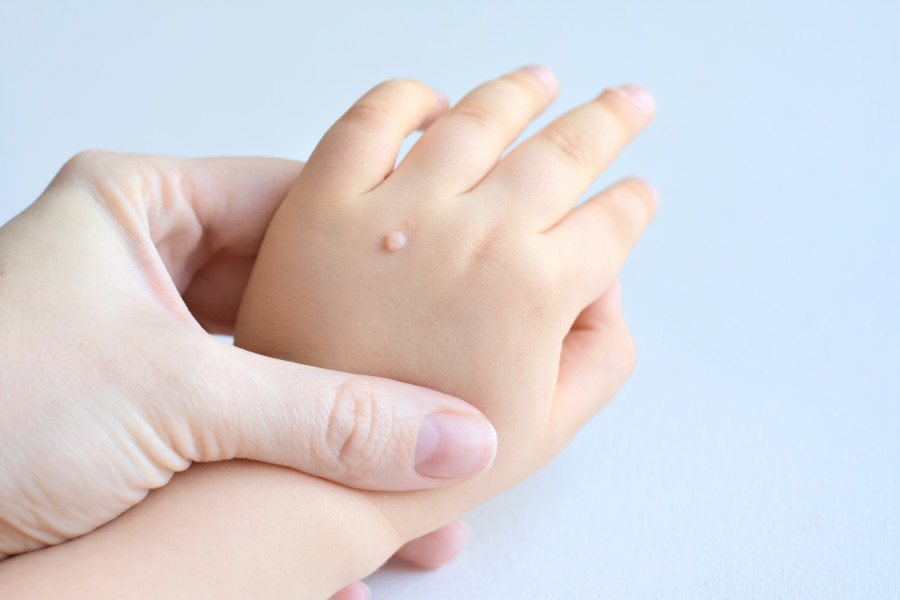
Rukusha Giri
A common skin condition many individuals encounter is warts—a benign growth, often misunderstood and highly contagious. They can appear anywhere on the body, including the tongue, and are especially common in children.

Dr Isha Poudel Koirala, a graduate of the Institute of Dermatology in Thailand, has spent eight years as a consultant dermatologist at the Kathmandu Clinic Of Cosmetic Surgery. Recently, she established her clinic, Aesthetic Aura Skin and Hair Clinic in Sankhamul. Here, she discusses warts as a skin disorder.
What are warts?
Warts are a skin condition characterised by rough, skin-coloured pimples that are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus spreads through contact with an infected person. Warts commonly appear on hands but can also be found on the face, feet, knees, and genitals. It’s important to note that there are different types of HPV; some are linked to serious health issues, like certain cancers.
Warts are common skin growths and usually don't pose significant health risks. HPV enters the skin through cuts or breaks, leading to the development of rough warts of various sizes and shapes. While anyone can get warts, children are more prone due to their frequent cuts and scrapes. Additionally, people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly or those with autoimmune diseases, are more vulnerable to HPV and, consequently, more likely to develop warts.
Are there different kinds of warts?
Yes, warts can appear in various forms depending on the affected body part. Common warts, also known as hand warts, are the most widespread. They typically emerge on the fingers and hands and are caused by HPV. Face warts, on the other hand, are flat or raised growths found on the face and forehead, sometimes appearing in clusters. Plantar warts develop on the soles of the feet and are often mistaken for calluses. These warts have small black dots in the centre and can be quite painful, usually occurring in groups and are challenging to remove.
In the realm of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), genital warts pose a significant threat as they can appear on the penis, vagina, or rectum. These warts stem from specific strains of HPV and are highly contagious through sexual contact. While they can be treated, ignoring them can lead to severe health complications. Periungual and subungual warts are another type that can form around or under fingernails and toenails. They can cause discomfort and pain when touched and, like other warts, are caused by HPV. They are very persistent, so it’s essential to seek timely medical attention for their removal.
What causes them?
Warts are highly contagious and spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated items like towels, doorknobs, or shower floors. The virus can also move from one part of the body to another, so it's vital to avoid touching warts and keep them covered. Genital warts can be transmitted through sexual activity, while habits like nail biting, cuticle picking, and shaving can create openings in the skin, allowing the virus to enter. To prevent HPV transmission and wart formation, it's essential to maintain good hygiene and avoid contact with infected individuals and contaminated objects.
How can they be treated?
Warts can be treated at home with over-the-counter ointments. However, it’s crucial to be aware of the risk of misdiagnosis, as some skin growths might look like warts but could be something else. Salicylic acid, a readily available treatment in gel, liquid, or plaster form, is effective against warts. To use it, apply the salicylic acid daily to the affected area after soaking it in warm water.
Warts can also transmit through direct skin contact with an infected individual. So, it's highly recommended to avoid contact with infected individuals and maintain good hygiene. If it continues to grow despite these measures, consulting a dermatologist is advisable.




 17.15°C Kathmandu
17.15°C Kathmandu









.jpg&w=300&height=200)




